Traders are warning governments to anticipate a lot larger borrowing prices over the approaching years, in a shift that can pinch public funds and constrain states’ capability to answer crises.
Regardless of a current rally, authorities bond costs have dropped exhausting on either side of the Atlantic this yr, partially reflecting a rising acceptance that rates of interest might want to keep excessive for the lengthy haul to dampen inflation. As well as, traders are struggling to digest governments’ a lot larger debt issuance plans with out central banks stepping in to vacuum up provide.
The result’s a lot larger bond yields that tie governments in to giant common curiosity funds once they tackle contemporary debt. In 2018, the curiosity invoice for G7 international locations stood at $905bn a yr, in line with credit standing company S&P. By 2026 it will likely be $1.5tn.
“Traders have at all times frightened about authorities debt and it’s by no means been an issue, however this time it feels prefer it’s for actual,” mentioned Jim Leaviss, chief funding officer of public fastened revenue at M&G Investments.
Increased for longer

That is the second in a sequence of articles in regards to the influence of excessive rates of interest throughout companies, governments and economies round the globe.
Half 1: Personal fairness takes a success
Half 2: Authorities funds and the influence on markets
Half 3: Reverberations within the company world
Half 4: The results for asset administration and rising markets
“We’re not simply frightened in regards to the quantity of presidency borrowing for regular stuff like healthcare spending and pensions,” he mentioned. As a substitute, he’s frightened about “structural” points resembling the scale of debt curiosity funds, the influence of central banks shrinking their very own bond holdings and the massive 31 per cent slice of US authorities bonds that can should be refinanced subsequent yr.
The yield on benchmark US Treasuries has risen by about 3 share factors previously two years to roughly 4.5 per cent, and final month it rose above 5 per cent. Economists surveyed by Bloomberg now anticipate these 10-year bonds will yield about 4.5 per cent on the finish of 2025, up from earlier expectations of three.5 per cent at first of July.
Elevated debt ranges have been on the forefront of conversations on the annual IMF and World Financial institution conferences in Marrakech final month, with the top of fiscal affairs on the Fund, Vitor Gaspar, telling the Monetary Occasions that rising debt servicing prices for governments can be a “persistent development” over the medium time period and have a “lasting impact”.
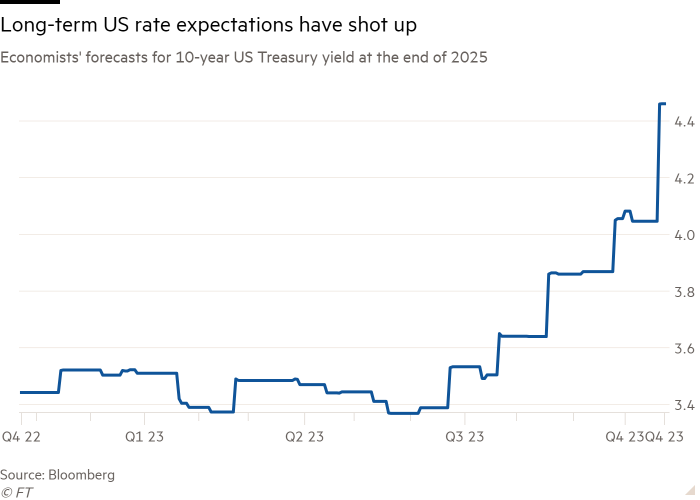
Over a long time, traders and governments have turn out to be accustomed to a reasonably dependable sample in rates of interest. Usually, central banks push them as much as dampen inflation, however rapidly reduce them once more when economies decelerate.
Now, it’s turning into more and more clear {that a} return to the post-2008 period of rates of interest near zero per cent is unlikely. The longer-term outlook for charges is very contested, however components that might preserve them up embrace excessive ranges of public borrowing together with big funding in tasks such because the inexperienced transition and infrastructure.
As well as, central banks are now not stepping in to maintain borrowing prices down by shopping for bonds in quantitative easing programmes; as a substitute they’re lowering the scale of their steadiness sheets via quantitative tightening.

“We’re principally transitioning from markets that have been engineered by central banks via QE to markets which might be much less engineered by central banks as a result of they’re now doing QT, and on the similar time there’s much more fiscal activism so there’s much more issuance and the market wants to soak up that,” mentioned Guillermo Felices, international funding strategist at PGIM Fastened Revenue.
“We now have left that period [of zero rates] behind us,” mentioned Stephen Millard, a deputy director of the Nationwide Institute of Financial and Social Analysis in London.
The IMF says international public debt is on target to strategy 100 per cent of gross home product by the tip of the present decade. Among the many largest drivers is the US, the place the federal government deficit is on observe to exceed 8 per cent of the nation’s GDP this yr.
“One thing should give to steadiness the fiscal equation,” the IMF warned about international money owed. “Coverage ambitions could also be scaled down or political pink strains on taxation moved if monetary stability is to prevail.”
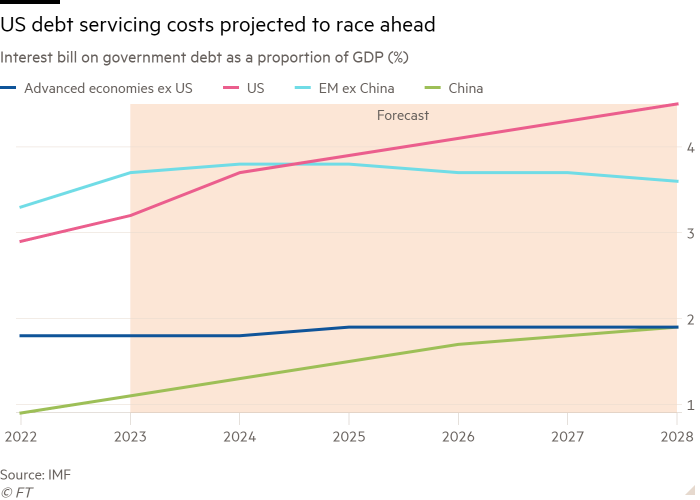
The US, which has the very best central financial institution fee within the G7 and a low income base in contrast with its higher-tax friends, is on target for a dramatic surge in debt servicing prices. Invoice Foster, senior vice-president at score company Moody’s, estimates that US curiosity bills as a proportion of presidency income will soar from underneath 10 per cent in 2022 to 27 per cent by 2033.
The anticipated soar in curiosity funds is extra acute within the US than in another international locations due to the quantity of Treasury bonds that can should be rolled over in 2024, which is prone to result in considerably larger authorities curiosity funds. Congressional Finances Workplace forecasts counsel that internet curiosity spending shall be near half of America’s general deficit by 2026.
Traders doubt whether or not the US can develop its option to a decrease debt burden. Financial progress forecasts for subsequent yr are anaemic at simply 1.5 per cent, whereas benchmark inflation-adjusted yields stand at near 2.2 per cent. “That’s primarily telling you that there may be an issue going ahead if rates of interest keep this excessive,” mentioned Felices.
“If the market smells that fiscal sustainability is underneath menace then they may push governments to some form of adjustment . . . by demanding the next threat premium to personal their debt,” he added.

A deluge of recent debt hitting markets can also be weighing on bond costs, significantly within the US. The Treasury market is roughly $25tn in dimension immediately, 5 occasions what it was in 2008.
“The market is considering, grasp on a minute, there’s completely no urge for food or visibility on any fiscal belt tightening at any level within the close to future,” mentioned Rohan Khanna, head of euro charges technique at Barclays. In truth, spending may be anticipated to develop with elections developing within the US, Germany, France and the UK subsequent yr, Khanna added.
The unsure outlook can also be placing some traders off proudly owning long-dated bonds, given the dangers that geopolitical tensions will result in better army spending and better prices of relocating strategic industries.
“Governments have to understand that the uncertainty in regards to the long-term charges has simply blown up [increased a lot],” mentioned Tomasz Wieladek, chief European economist at asset supervisor T Rowe Value. “They must be extra prudent going forwards as there are dangers that the debt servicing turns into unmanageable.”

Policymakers have at the very least sounded extra cautious about America’s mounting obligations now that it boasts a debt-to-GDP ratio of roughly 98 per cent. Jay Powell, chair of the Federal Reserve, was the most recent official to boost considerations in regards to the US fiscal state of affairs.
“It’s not that the extent of the debt is unsustainable,” he mentioned in October. “It’s that the trail we’re on is unsustainable and we’ll must get off that path sooner fairly than later.”
Europe can also be grappling with surging debt prices, with fiscal considerations serving to to push up borrowing prices throughout the area. The UK was given a warning shot final yr when former chancellor Kwasi Kwarteng introduced a £45bn bundle of unfunded tax cuts, sparking turmoil within the bond market and resulting in intervention by the Financial institution of England.
The UK has additionally skilled a pointy rise in curiosity prices, on condition that round 25 per cent of its debt is in inflation-linked bonds. Debt curiosity spending reached 4.4 per cent of nationwide revenue in the latest fiscal yr within the UK, greater than double the common of two per cent over the primary twenty years of this century.

In keeping with the Institute for Fiscal Research think-tank, it should keep at or above 3 per cent of GDP over the medium time period, £26bn a yr larger than earlier ranges. Ranking company Fitch estimates curiosity prices shall be 10.4 per cent of presidency revenues this yr, up from a median of 6.2 per cent between 2017 and 2021.
Within the EU, a number of international locations have a finances deficit larger than the bloc’s 3 per cent restrict, which is ready to turn out to be efficient from January after it was suspended in the course of the pandemic.
Considerations are additionally mounting in Italy. The hole between benchmark Italian and German borrowing prices surged by 0.3 share factors to greater than 2 per cent after Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni’s authorities raised its fiscal deficit targets and reduce its progress forecast for this yr and subsequent. Nevertheless, it has since narrowed once more as a part of a wider bond market rally.
“Deficits are why individuals speak about bond vigilantes coming again — the concept that bond markets will act as a constraint on fiscal spending,” Leaviss mentioned.

