Nigerians are turning to costly emergency loans to cowl the price of necessities, because the nation’s financial woes push extra individuals into poverty and fears develop of a client debt disaster.
Excessive inflation and a controversial austerity drive by the federal government have weighed down on Nigerians’ incomes at a time when payday mortgage suppliers have turn out to be ubiquitous.
“You turn out to be enslaved,” mentioned Samuel, the proprietor of a small dry cleansing firm in Lagos who declined to present his surname due to the stigma hooked up to borrowing in Nigeria. At one level he owed cash to 4 totally different fintechs at rates of interest as excessive as 40 per cent and was paying again one mortgage with credit score from one other.
The tripling of the price of petrol since Might, following President Bola Tinubu’s elimination of $10bn-worth of gasoline subsidies, had meant he had “no selection however to borrow”, he mentioned.

Current inflation information highlighted the pressures going through odd Nigerians. Meals costs are 31.5 per cent larger than they had been final yr. Bus fares in Nigerian cities have on common risen 117 per cent yr on yr, in accordance with the newest information from the statistics company.
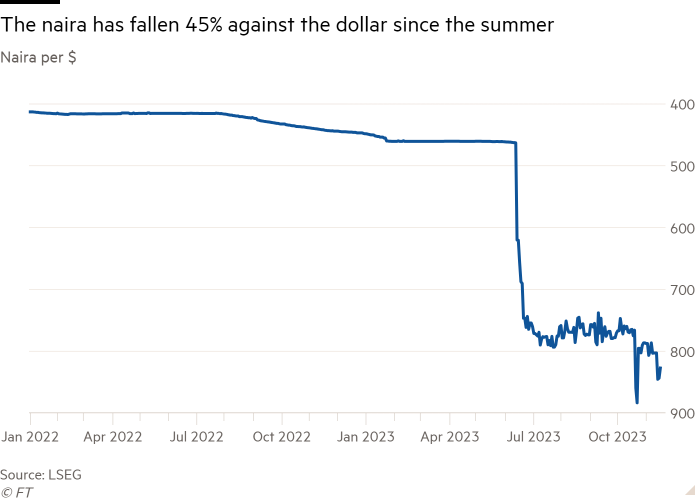
The depreciation of the naira has additionally pushed up prices within the import-dependent financial system, contributing to an general rise in client costs of 27.3 per cent within the yr to October — the nation’s highest inflation degree for 20 years.
The World Financial institution mentioned this yr that “entrenched inflation” had pushed a further 4mn Nigerians into poverty. Some 63 per cent, or about 133mn individuals, had been already “multidimensionally poor”, in accordance with authorities statistics, creating fertile circumstances for lenders to capitalise on.
The nation now has nearly 200 licensed on-line lenders, in accordance with Nigeria’s Federal Competitors and Client Safety Fee, with extra believed to be working illegally.
The apps of market leaders OKash and Palmcredit have greater than 5mn downloads.
Many lenders try to disgrace debtors into repaying their loans by messaging individuals of their telephone contacts saying they’re in default.
Customers of OKash are required to grant the apps entry to their contacts, location, SMS, calendar and digital camera once they enroll. The corporate says on their web site that that is “an important a part of analysis course of”.
Palmcredit says in its phrases and circumstances that it requires entry to customers’ telephone historical past, system identification, contact record, name and textual content historical past, and different information. It additionally warns that it “has the precise to alarm contacts to declare the mortgage if you’re late together with your fee”.
OKash and Palmcredit didn’t reply to requests for remark.
On-line lenders usually present loans with out the collateral necessities of most established banks and infrequently cost charges nicely in extra of Nigeria’s key rate of interest of 18.75 per cent and the utmost lending price of 27.24 per cent for high-street lenders.
Central financial institution information final week confirmed lending from excessive road banks rose quickly over the second quarter. Whole client credit score, of which nearly three quarters had been private loans, elevated 12.2 per cent over the three months to June.
The official information doesn’t seize emergency lending from payday suppliers. However monetary literacy consultants and analysts mentioned they had been seeing rising numbers of individuals resorting to emergency funding to bridge the hole between their prices and their incomes.
A report by the Lagos-based SBM Intelligence consultancy confirmed that 27 per cent of Nigerians who had seen their pay decline had borrowed to enhance their earnings.
“The standard of life [of Nigerians] has decreased throughout all earnings classes,” mentioned Seyi Awojulugbe, senior analyst at SBM Intelligence, who co-led the report.
Oluwatosin Olaseinde, founding father of the monetary literacy service Cash Africa, mentioned financial difficulties had made many individuals “determined” and weak to “predatory lenders with excessive rates of interest”.
“When individuals can’t meet their quick wants internally or by means of assist from family and friends, they flip to exterior loans,” she mentioned, highlighting the proliferation of on-line lenders in Nigeria.

Oluwakemi Afuye, a seamstress, mentioned she had been inundated with texts to her telephone promoting immediate loans.
Whereas she has not borrowed from payday lenders after listening to horror tales of individuals being harassed once they default, the mom of 1 has resorted to wage advances from her employer to deal with the hovering value of meals and transport.
“You need to minimize your price range,” mentioned Afuye, who has switched to purchasing groceries at conventional markets the place they’re cheaper than the supermarkets she used to frequent. “The state of affairs is disheartening.”
The rise in the price of dwelling has led to calls by the nation’s labour unions to demand a minimal wage of not less than N100,000 ($122) a month, up from the present degree of N35,000. The unions have threatened to strike if their calls for should not met.
There may be additionally growing anger with the Tinubu authorities, which has been in place since Might, which residents criticise for extravagance at a time when they’re struggling to make ends meet.
Afolabi Adekaiyaoja, analysis analyst on the Abuja-based Centre for Democracy and Growth think-tank, mentioned there was a way amongst Nigerians that the austerity they had been being requested to abdomen was not practised by the federal government.
He pointed to the dimensions of Tinubu’s authorities, the biggest cupboard since Nigeria’s return to democracy in 1999, consisting of 48 ministers and greater than 20 particular advisers — one thing a senior member of the president’s All Progressives Congress occasion blamed on “political IOUs” to pay again favours dished out throughout a bruising election marketing campaign.
“The problem with the federal government calling on residents to bear financial sacrifices . . . is that it’s at odds with its spending,” mentioned Adekaiyaoja. “The honeymoon is over and the federal government can’t afford to worsen an already delicate state of affairs for Nigerians.”
The federal government’s supplementary price range, authorized by parliament and signed into regulation by the president on November 8, was met with uproar.
It included N1.5bn ($1.9mn) for automobiles for the workplace of the primary girl, N2.9bn ($3.7mn) for the renovation of the president’s dwelling quarters and one other N28bn ($35.6mn) for different prices, together with the president’s buy of luxurious automobiles.
“It doesn’t make sense,” mentioned electrician Kenny Ogunbela. “These items are too costly and it exhibits they don’t care in regards to the individuals.”

