This submit estimates “comfort yields” for presidency debt in ten of the G11 currencies based mostly on evaluation from a current paper. As in our companion submit, we measure comfort yields with option-implied field fee information that’s estimated from choices traded on the principle inventory market index in every nation. We discover {that a} nation’s common comfort yield is intently associated to its stage of rates of interest. As well as, we discover that common coated curiosity parity (CIP) deviations are roughly the identical throughout international locations when they’re measured with field charges. We rationalize these findings with a mannequin through which comfort yields rely upon home monetary intermediaries, however CIP deviations rely upon worldwide arbitrageurs funded with greenback debt.
Estimating Worldwide Comfort Yields
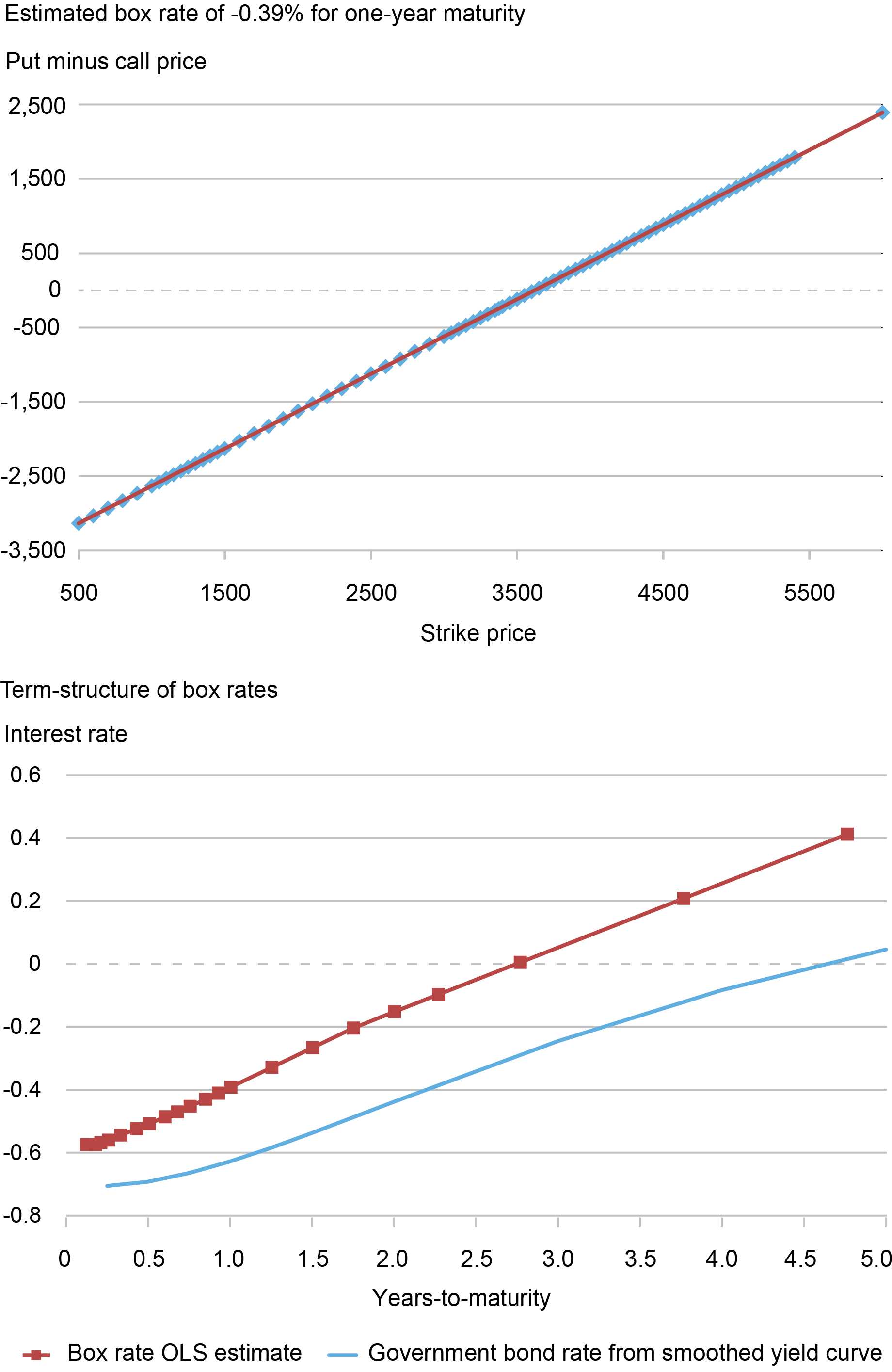
We illustrate our method for estimating international field charges utilizing possibility quotes for the Euro Stoxx 50 index, that are denominated in euros. The worldwide estimates construct upon a current paper which estimates field fee information for the USA, that are denominated in {dollars}. The chart under presents an instance of estimating the term-structure of field charges on March 15, 2022. The highest plot exhibits a regression of put minus name costs onto strike costs for choices expiring one-year afterward March 17, 2023. The field fee implied by the slope coefficient is -.39 p.c. As in our companion submit on SPX choices denominated in {dollars}, put-call parity holds virtually precisely for Stoxx choices with an ordinary error of the field fee estimate that’s lower than .01 p.c or one foundation level on this instance. Increasing the evaluation to different maturities, the underside plot reviews the yield curve for field charges in comparison with authorities bond charges. There’s a optimistic unfold between field charges and the federal government bond yield curve throughout maturities, with a ramification of round 25 foundation factors at a 1-year maturity.
Estimating Field Charges for the Euro
Supply: OptionMetrics and European Central Financial institution.
Word: The highest panel plots put minus name settlement costs for a similar strike worth and maturity on March 15, 2022 alongside fitted values from an unusual least squares (OLS) regression. The field fee implied by the slope coefficient from the regression is -0.39 p.c for a maturity in 367 calendar days on March 17, 2023. The underside panel plots the term-structure of field charges alongside estimates of presidency bond charges from a smoothed AAA-rated yield curve from the European Central Financial institution. All charges are zero-coupon low cost charges with steady compounding. Years-to-maturity is precise calendar days divided by 365. The choice information is from OptionMetrics for Euro Stoxx 50 index choices with maturities between 1 month and 5 years.
Euro Comfort Yields Over Time
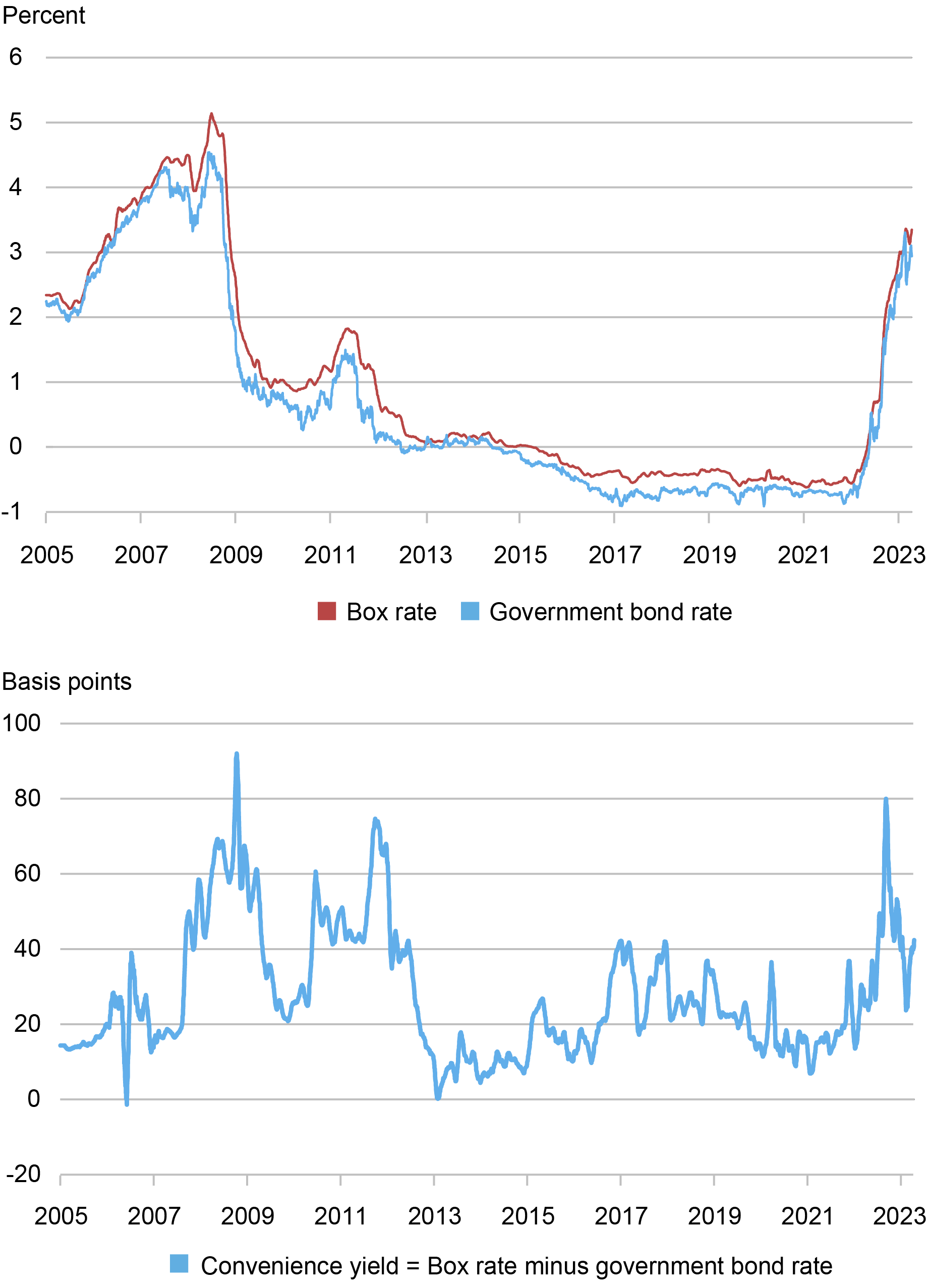
We plot the time collection of Euro field charges, authorities bond yields, and implied comfort yields within the chart under. The comfort yield is the distinction between the field and authorities bond charges, exhibiting the speed of return traders forgo to carry authorities debt in comparison with a much less money-like asset with similar cashflows. The 2 charges observe one another intently, though their distinction tends to develop throughout crises such because the 2007-09 monetary disaster and the 2011-12 European debt disaster, and throughout the financial tightening cycle that began in 2022.
Time-Sequence of 1-12 months Field Fee and Comfort Yield for the Euro
Supply: OptionMetrics and European Central Financial institution.
Word: The chart plots the 1-year field fee, authorities bond fee, and comfort yield estimate from January 2005 by April 2023 as a 21-day shifting common throughout buying and selling days. The field fee is estimated by unusual least squares from put-call parity. To acquire a continuing 1-year maturity, we linearly interpolate the closest STOXX 50 index possibility maturities whose put-call parity regressions have an R-squared of a least 0.99999 out to 5 nines. Authorities bond charges are from a smoothed yield curve to acquire a 1-year fixed maturity zero-coupon fee. Each charges are zero-coupon low cost charges with steady compounding. Outcomes are comparable utilizing the Theil-Sen estimate of the field fee from the field unfold commerce.
Comfort Yields Versus Curiosity Charges
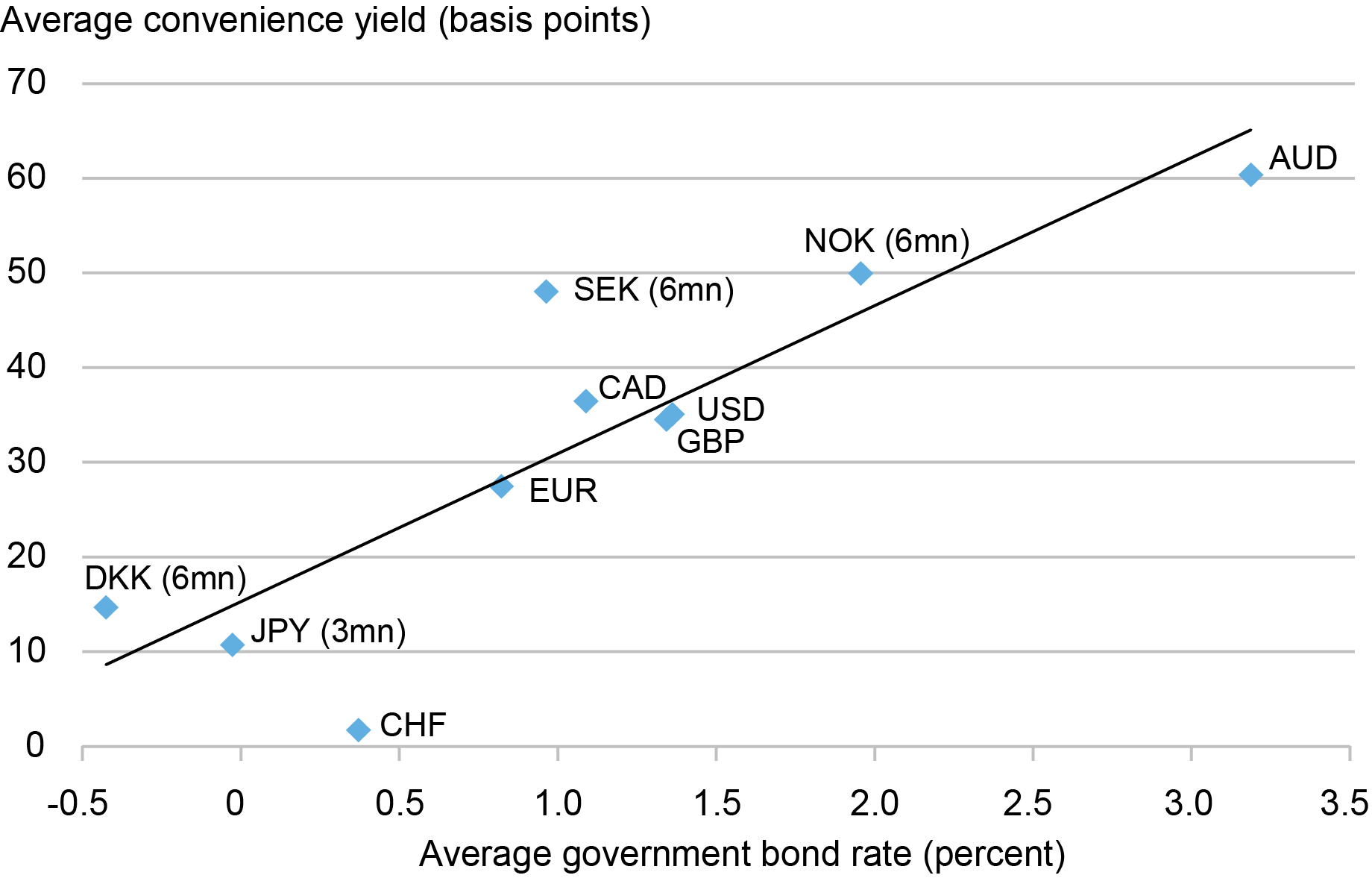
The cross-section of comfort yields in numerous international locations is well-explained by the extent of nations’ rates of interest. The chart under reviews a scatter plot of pattern common comfort yields measured with the field fee versus pattern common authorities bond charges for various currencies. There’s a robust affiliation between comfort yields and rates of interest, with a 1 p.c greater rate of interest comparable to a 15 foundation level bigger comfort yield on common. In our paper we discover that comfort yields throughout international locations are usually not properly defined by different components, corresponding to authorities debt-to-GDP ratios or sovereign credit score default swap spreads. Our outcomes are associated to a current examine that additionally finds a relationship between comfort yields and rates of interest in U.S. time-series information. We complement the time-series method with our outcome within the cross-section of nations.
The robust relationship between the extent of rates of interest and comfort yields might be defined by traders selecting to substitute between money and different sources of liquidity. The liquidity premium/comfort yield of money is the same as the nominal rate of interest. For instance, if rates of interest are 4 p.c, holding money for one yr will value you 4 cents of revenue per greenback. Secure property corresponding to authorities debt which are extremely liquid and money-like function shut substitutes for money. This implies that comfort yields for secure property shall be intently associated to the chance value of money and therefore the extent of rates of interest.
International locations with Larger Curiosity Charges Have Larger Comfort Yields
Supply: Intercontinental Trade (ICE), Thomson Reuters Tick Historical past Knowledge, and OptionMetrics.
Word: The chart plots common comfort yield in opposition to common authorities bond fee from January 2004 to July 2020 for the accessible pattern interval for every forex that’s reported within the paper. The comfort yield is the 1-year field fee minus the 1-year authorities bond fee in all international locations besides Norway, Sweden, and Denmark the place we use 6-month charges and Japan the place we use 3-month charges for a bigger pattern of observations of exactly estimated field charges to measure comfort yields. Field charges are estimated from intraday time-stamped possibility quotes from the Intercontinental Trade (ICE) which are supplemented with intraday Thomson Reuters Tick Historical past information after which with OptionMetrics each day information as wanted. For every forex and maturity, we run the put-call parity regressions minute-by-minute and compute the median field fee for every day and maturity. To reduce the influence of outliers, we solely use regressions with an R-squared of at the least 0.99999 out to 5 9s. To acquire fixed maturity charges, we linearly interpolate between the closest maturities.
Comfort Yields and Coated Curiosity Parity
The robust relationship between comfort yields and rates of interest can doubtlessly clarify well-known information about CIP deviations. CIP is a no-arbitrage relationship that states {that a} greenback secure asset ought to have the identical yield as an in any other case similar artificial asset constructed from a international secure asset with a forex swap. An vital anomaly within the post-financial-crisis period has been the rise of CIP deviations. This may increasingly mirror new frictions induced by post-2008 monetary laws that increase prices of doing arbitrage trades.
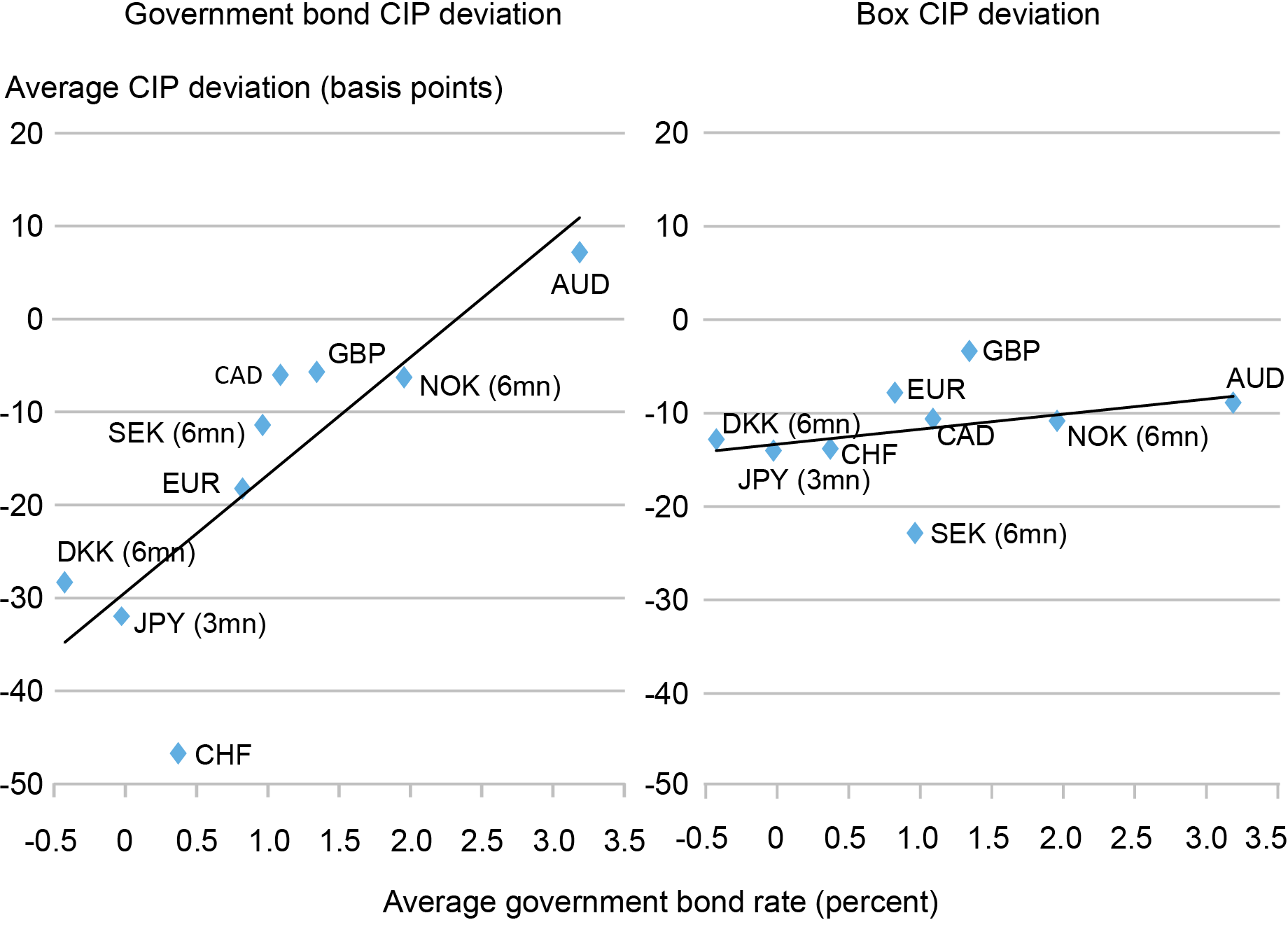
Earlier analysis has proven that there’s a robust correlation between CIP deviations and the extent of nominal rates of interest. In our paper, we present that the CIP deviation for a secure asset corresponding to authorities debt might be written because the sum of two phrases. The primary time period is the distinction between international locations’ secure asset comfort yields. The second time period is a CIP deviation constructed from our field charges, which we interpret as reflecting frictions in worldwide arbitrage, since this time period solely relies upon available on the market costs of monetary derivatives and is thus free from the comfort yield of secure property.
Within the chart under, we present the connection between CIP deviations and the extent of rates of interest. As in prior research, we discover a robust correlation between authorities bond CIP deviations and the extent of rates of interest. Nonetheless, we discover virtually no relationship between field fee CIP deviations and the extent of rates of interest. For the field fee, the greenback fee is round 10 foundation factors decrease than an artificial greenback rate of interest implied by a currency-hedged international field fee. This unfold may be very comparable throughout international locations, suggesting that there’s a roughly fixed value of worldwide arbitrage between the U.S. and one another nation in our information on common.
CIP Deviations Much less Correlated with Curiosity Charges When Measured with Field as Against Authorities Bond Charges
Supply: Intercontinental Trade (ICE), Thomson Reuters Tick Historical past Knowledge, and OptionMetrics.
Word: The chart plots the common CIP deviation for presidency bond charges (left panel) and for field charges (proper panel) in opposition to common authorities bond charges from January 2004 to July 2020 when information is on the market. The pattern interval for every forex is reported within the paper. The CIP deviation is computed for a 1-year maturity in all international locations besides Norway, Sweden, and Denmark the place we use 6-month charges and Japan the place we use 3-month charges for a bigger pattern of observations from which we estimate the common comfort yield.
Decoding the Worldwide Function of the Greenback
Two of our outcomes above relate to the particular position of the greenback in worldwide finance. First, we discover that the U.S. comfort yield is the fifth largest of ten international locations. After controlling for the extent of rates of interest, U.S. comfort yields are neither unusually giant nor small. Second, the U.S. field fee lies roughly 10 foundation factors under the greenback fee implied by a currency-hedged model of any international nation’s field fee. In our paper, we clarify these information with a theoretical mannequin the place the essential distinction between the greenback and different currencies is that worldwide monetary arbitrageurs are funded with dollar-denominated debt.
Throughout monetary crises, greenback comfort yields and CIP deviations each dramatically spike. A typical interpretation of those information is that dollar-denominated debt has a very giant comfort yield that’s particularly delicate to emphasize in monetary markets. In distinction to earlier work, we immediately measure international comfort yields and discover that also they are delicate to crises. As well as, we discover that field CIP deviations (which don’t mirror a comfort yield) additionally enhance in magnitude throughout crises. Our theoretical mannequin explains these information by having the greenback function the distinctive funding forex of worldwide arbitrage, quite than having greenback secure property with unusually giant comfort yields.
William Diamond is an assistant professor of finance at The Wharton College, College of Pennsylvania.

Peter Van Tassel is a monetary analysis economist in Capital Markets Research within the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York’s Analysis and Statistics Group.
cite this submit:
William Diamond and Peter Van Tassel, “A Take a look at Comfort Yields across the World,” Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York Liberty Road Economics, October 3, 2023, https://libertystreeteconomics.newyorkfed.org/2023/10/a-look-at-convenience-yields-around-the-world/.
Disclaimer
The views expressed on this submit are these of the creator(s) and don’t essentially mirror the place of the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York or the Federal Reserve System. Any errors or omissions are the duty of the creator(s).